
Overhaul and adjustment of crown block brakeAccording to the requirements of crane safety regulations, the brakes should be regularly inspected. During the installation, debugging, and use of the brake, special attention should be paid to the following adjustments:(1) Adjustment of braking torque: The braking torque must be adjusted according to the specified requirements, which is the basic work during the installation, debugging, and operation of the brake (checking for any changes). According to the standard requirements of the brake, the braking torque value should have a clear scale, and the torque value can be adjusted according to the scale or line of the torque value.(2) Adjustment of the working stroke of the driving device: The working stroke of the brake driving device should be adjusted at the working environment temperature, and its rated working stroke value should be indicated in the product manual or on the driving device. During use, it is necessary to regularly observe the changes in the working stroke based on the frequency of use. Especially for brakes without an automatic compensation mechanism for brake pad wear, the working stroke of the driving device must not be equal to its maximum stroke (rated stroke), otherwise serious consequences of loss of braking force will occur. When stopping after use, the compensation stroke of the driving device should be checked (the rated stroke of the driving device minus its working stroke). If the compensation stroke is too small, it should be adjusted immediately to avoid reducing the compensation stroke and losing braking force due to cooling deformation caused by thermal expansion of the brake pad during use.(3) Adjustment of compensation mechanism: The installation of automatic compensation mechanism for brake pad wear (referred to as compensation mechanism) on the brake can avoid frequent adjustment of the working stroke of the driving device during the use of the brake. However, the compensation mechanism should be adjusted and reliably fixed, otherwise if the working stroke of the driving device is not adjusted in a timely manner after the brake pad is worn, the braking force will be lost. The adjustment of the compensation institution should be made according to the product manual, and regular observation should be made to see if there are any changes during use.(4) Adjustment of backlash: After the working stroke of the brake drive device is adjusted, the total backlash of the brake pad is also determined accordingly. The backlash on each side of the brake pad should be basically equal to avoid friction caused by large backlash on one side and "unable to open" on the other side, which can cause a sharp increase in unilateral friction temperature, reduce braking performance, and exacerbate wear of the brake pad. Therefore, the backlash should be adjusted according to the product manual.Electric hydraulic brakeYWZB YWZ3B YWZ4B YWZ5 YWZ8 YWZ9 YWZ12 YWZ13 YW YWL TYWZ2 YWPElectromagnetic block brakeJZ (TJ2A) MW (Z) ZWZAZWZ2 ZWZ3ADCW3Electromagnetic failure protection disc brake5SE 561SE 560SE 56SEDCPZ12.7 4SE 3SE ST1SE ST2SE 450SEHydraulic failure protection disc brake5SH 4SH 3SH 450SH ST1SH ST2SH ST3SH ST4SHSB (YQP) SBDST5SH ST10SHST16SHST25SHST25SH-AST40SH904SHSBBElectro hydraulic arm disc brakeYPZ2 I, II, IIIYPZ2 IV, V, VIPneumatic caliper disc brake QP12.7 5SP4SP3SP450SPPDADP60M-ADP61M-ADP62MHydraulic direct acting disc brake DADH75ADH60ADH90ADH120DADH80DADH90DADH120DADH103DADH195Electric hydraulic thrusterYT1 EdMYT1 hydraulic thruster motor modelBO62Z YDT80-2 ASF82A ASF102A B112Z A028012A028022 three-phase asynchronous motorExplosion proof electric hydraulic thrusterBYT1 BED
time:2021-10-14
More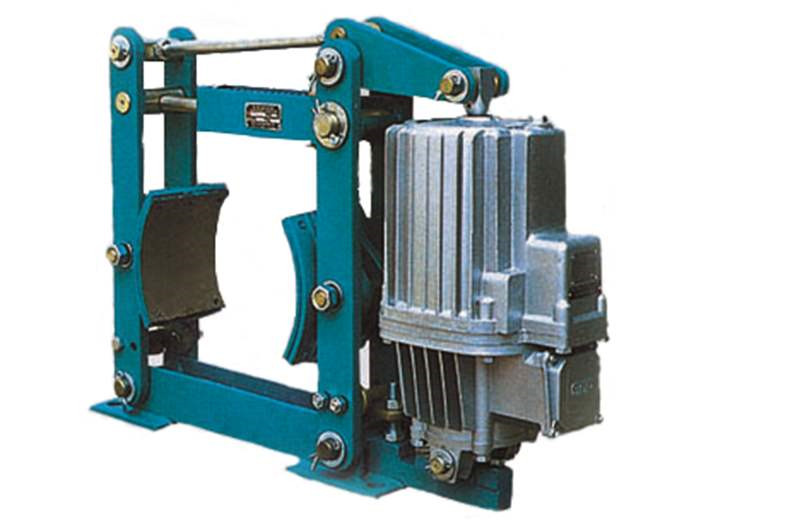
Overhaul and adjustment of crown block brakeAccording to the requirements of crane safety regulations, the brakes should be regularly inspected. During the installation, debugging, and use of the brake, special attention should be paid to the following adjustments:(1) Adjustment of braking torque: The braking torque must be adjusted according to the specified requirements, which is the basic work during the installation, debugging, and operation of the brake (checking for any changes). According to the standard requirements of the brake, the braking torque value should have a clear scale, and the torque value can be adjusted according to the scale or line of the torque value.(2) Adjustment of the working stroke of the driving device: The working stroke of the brake driving device should be adjusted at the working environment temperature, and its rated working stroke value should be indicated in the product manual or on the driving device. During use, it is necessary to regularly observe the changes in the working stroke based on the frequency of use. Especially for brakes without an automatic compensation mechanism for brake pad wear, the working stroke of the driving device must not be equal to its maximum stroke (rated stroke), otherwise serious consequences of loss of braking force will occur. When stopping after use, the compensation stroke of the driving device should be checked (the rated stroke of the driving device minus its working stroke). If the compensation stroke is too small, it should be adjusted immediately to avoid reducing the compensation stroke and losing braking force due to cooling deformation caused by thermal expansion of the brake pad during use.(3) Adjustment of compensation mechanism: The installation of automatic compensation mechanism for brake pad wear (referred to as compensation mechanism) on the brake can avoid frequent adjustment of the working stroke of the driving device during the use of the brake. However, the compensation mechanism should be adjusted and reliably fixed, otherwise if the working stroke of the driving device is not adjusted in a timely manner after the brake pad is worn, the braking force will be lost. The adjustment of the compensation institution should be made according to the product manual, and regular observation should be made to see if there are any changes during use.(4) Adjustment of backlash: After the working stroke of the brake drive device is adjusted, the total backlash of the brake pad is also determined accordingly. The backlash on each side of the brake pad should be basically equal to avoid friction caused by large backlash on one side and "unable to open" on the other side, which can cause a sharp increase in unilateral friction temperature, reduce braking performance, and exacerbate wear of the brake pad. Therefore, the backlash should be adjusted according to the product manual.Electric hydraulic brakeYWZB YWZ3B YWZ4B YWZ5 YWZ8 YWZ9 YWZ12 YWZ13 YW YWL TYWZ2 YWPElectromagnetic block brakeJZ (TJ2A) MW (Z) ZWZAZWZ2 ZWZ3ADCW3Electromagnetic failure protection disc brake5SE 561SE 560SE 56SEDCPZ12.7 4SE 3SE ST1SE ST2SE 450SEHydraulic failure protection disc brake5SH 4SH 3SH 450SH ST1SH ST2SH ST3SH ST4SHSB (YQP) SBDST5SH ST10SHST16SHST25SHST25SH-AST40SH904SHSBBElectro hydraulic arm disc brakeYPZ2 I, II, IIIYPZ2 IV, V, VIPneumatic caliper disc brake QP12.7 5SP4SP3SP450SPPDADP60M-ADP61M-ADP62MHydraulic direct acting disc brake DADH75ADH60ADH90ADH120DADH80DADH90DADH120DADH103DADH195Electric hydraulic thrusterYT1 EdMYT1 hydraulic thruster motor modelBO62Z YDT80-2 ASF82A ASF102A B112Z A028012A028022 three-phase asynchronous motorExplosion proof electric hydraulic thrusterBYT1 BED
time:2021-10-14
More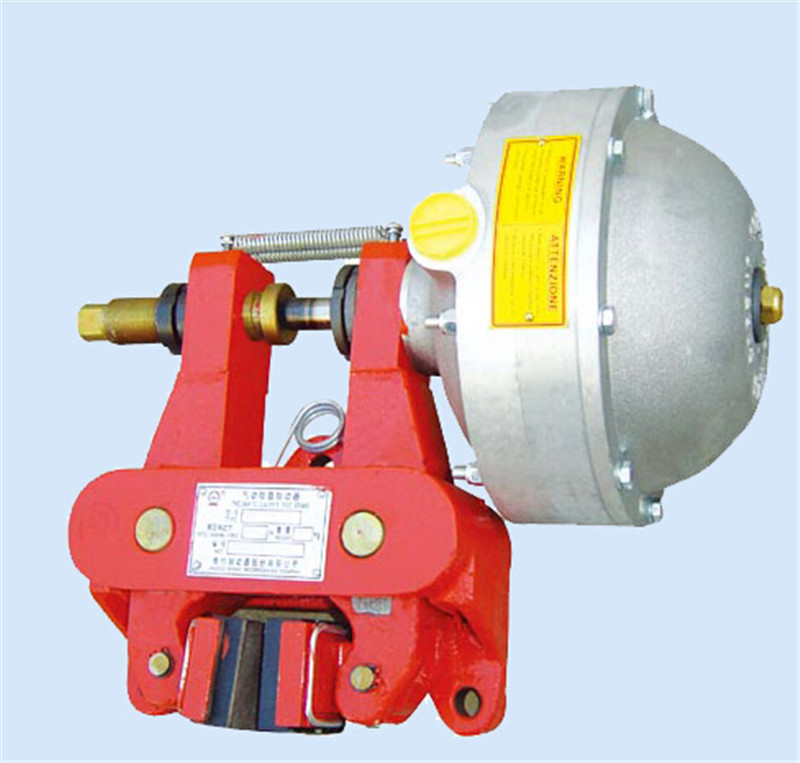
QP12.7 Pneumatic BrakeQP series pneumatic caliper disc brakeQP12.7 Pneumatic Brakes QP12.7-A, QP12.7-B, CQP12.7-A, CQP12.7-B, QPL12.7, QP20, QP25, QP30 and other series modelsJiaozuo Brake Co., Ltd. has a complete range of pneumatic disc brakes with safe and reliable performance, smooth braking, high action frequency and long service life.QP12.7 Pneumatic BrakeQP12.7 pneumatic inlaid disc brake friction plate is an advanced product that not only has the advantages of disc brake, but also has extensive adaptability and unique advantages. This product has the characteristics of simple structure, small size, light weight, high reliability, using compressed air as the power source, convenient use, suitable for multiple disc diameters, convenient installation, debugging, and maintenance. Widely used for deceleration and braking of fixed operating mechanisms such as metallurgy and bulk loading and unloading;QP12.7 Pneumatic brake QP12.7 Pneumatic inlaid disc brake has QP12.7-A, QP12.7-B and other specifications. One disc diameter of each type of brake can be adjusted for four levels of braking torque. The matching air bag adopts imported aluminum alloy air bag, which has reliable and stable performance, good sealing performance, small size and light weight. It can be divided into Type A and Type B according to the use performance requirements;The QP12.7 pneumatic brake pad adopts a pressure spring clamp type, with a unique structure and convenient and fast replacement;Can be equipped with a display device to directly display the working status of the brake;All power sources of the QP12.7 pneumatic brake do not need to be set separately, and can be used in conjunction with existing air compression stations. A speed regulating valve is installed in the gas supply line, and the braking time can be adjusted steplessly.QP12.7 Pneumatic Brakes YWZ, YWZ3, YWZ4, YWZ5, YWZ8, YWZ10, YWZ9, YWZ13, YW Series Electric Hydraulic BrakesJZ, MW, TJ2, ZWZA, ZWZ3 series electromagnetic brakesQP, CQP series pneumatic caliper disc brakeQP12.7 Pneumatic Brake DCPZ Series Electromagnetic Caliper Disc BrakeYPZ series arm disc brakeQP12.7 Pneumatic Brake SBD Series Safety BrakeSH, ST series hydraulic failure protection brakeDADH series hydraulic direct acting brakeQP12.7 Pneumatic Brake SE Series Electromagnetic Failure Protection BrakeSP series pneumatic failure protection brakeYFX, YDGZ, YLBZ, Series Windproof BrakesQP12.7 Pneumatic Brake1、 Working principleQP12.7 pneumatic brake QP12.7 pneumatic caliper Disc brake frame and cylinder are composed of two parts (see the structure diagram). When cylinder 1 is filled with pressure air, piston rod 5 quickly contracts into the cylinder under the action of air pressure. The left and right brake arms, under the action of return spring 4, drive the friction block 12 to quickly open (i.e. release the brake). When the cylinder stops supplying air and quickly deflates through the control valve, the piston rod 5 quickly extends under the internal spring of the cylinder, pushing the left and right brake arms to drive the friction block 12 to close (i.e., the holding brake).QP12.7 Pneumatic Brake II. Installation of Brake1. Firstly, check the brake surface of the brake disc and brake pad for oil sludge or other stains.2. Install the G3/8 "(cast iron rod cylinder) or 1/2" (cast aluminum cylinder) connector on the air inlet of cylinder 1, connect the air pipe with a hose, and the air source should be free of oil, water, and other impuritiesQP12.7 Pneumatic Brake 3. When installing, first introduce pressure air to retract the piston rod 5 into the cylinder. Then, install the friction block 12 into the brake disc in the direction perpendicular to the brake disc. Then, fix the base 9 horizontally on the rigid base so that its center is in line with the thickness center of the brake disc. The installation position dimensions are shown in the structural diagramQP12.7 Pneumatic Brake III. Adjustmenta) Adjust the air pressure value to a range of 5-7 bar.b) For normal work, the first step is to test the brake several times and check if there are any abnormalities in the brake.c) The retraction distance of the friction block can be adjusted by rotating the adjustment rod 6 to change the size of the working stroke. When rotating the adjustment rod, pressure air is first introduced to retract the piston rod, and then adjusted.QP12.7 Pneumatic Brake IV. MaintenanceWhen the friction plate of QP12.7 pneumatic brake is worn and the working stroke increases to 8mm, it is necessary to immediately adjust the rod 6 to readjust the working stroke by about 4mm. Otherwise, the brake will fail. After adjustment, the nut 7 should be tightened. When the friction block 12 is worn to about 6mm, the wear block needs to be replaced. The replacement steps are as follows:QP12.7 Pneumatic brake 1, cylinder,2. Right brake arm3. Return spring5. Piston rod6. Adjusting the lever7. Nut8. Left brake arm9. Base10. Brake pads11. Spring steel wire12. Friction blockQP12.7 Pneumatic Brake Application:QP12.7 Pneumatic Brake QP series pneumatic caliper disc brake is mainly used for braking and deceleration of various mechanisms in hoisting, transportation, metallurgy, mining, port, construction and other machinery, as well as tension control of machinery such as cable, paper making, steel plate and so on.
time:2021-10-14
More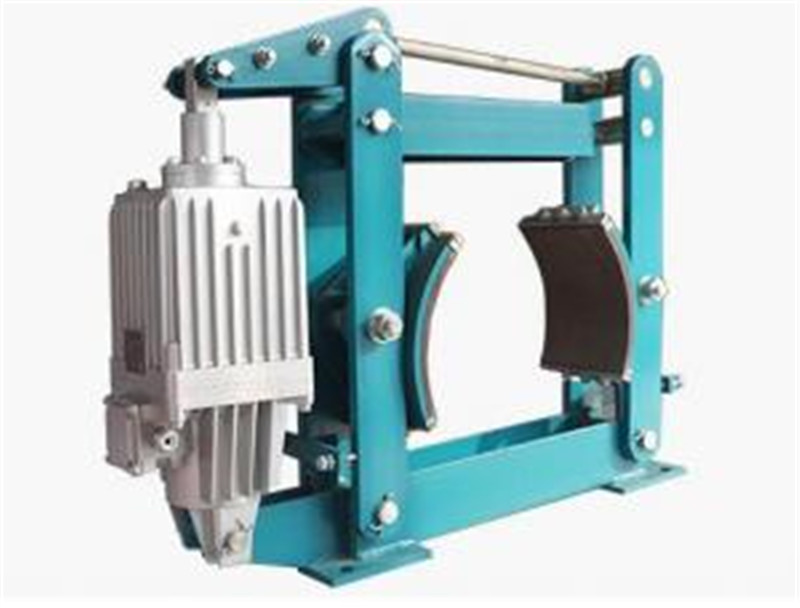
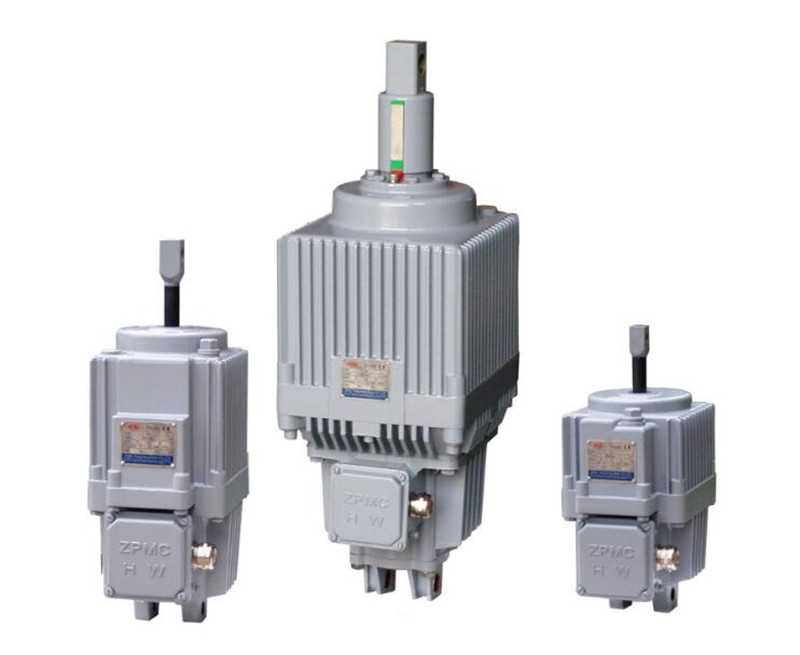
Ywz-400/90 YWZ4-400/121 ED, YT1 series electric hydraulic thruster YTYWZ-100/18,YWZ-200/25,YWZ-300/25,YWZ-300/45,YWZ-300/90,YWZ-400/45,YWZ-400/90YWZ-500/125,YWZ-600/180YWZ series electric hydraulic block brakes: YWZ-100/18, YWZ-200/25, YWZ-300/25, YWZ-300/45, YWZ-300/90YWZ-400/45, YWZ-400/90, YWZ-500/125, YWZ-600/180YWZ5-630/121 YWZ5-500/201 YWZ5-500/121 YWZ5-500/80 YWZ5-400/121 YWZ5-400/80YWZ5-400/50 YWZ5-315/80 YWZ5-315/50 YWZ5-315/30 YWZ5-315/23 YWZ5-250/50YWZ5-250/30 YWZ5-250/23 YWZ5-200/30 YWZ5-200/23 YWZ5-160/23YMZ4-800/301 YMZ4-700/301 YMZ4-600/201 YMZ4-600/121 YMZ4-500/201YMZ4-500/121 YMZ4-400/121 YMZ4-400/80 YMZ4-400/50 YMZ4-300/80YMZ4-300/50 YMZ4-300/30 YMZ4-200/30 YMZ4-200/23 YMZ4-150/23 YMZ4-100/23YT125z/4, YT1-45/6 YT190/8 YT1-125Z/10 YT1-180/12
time:2021-10-14
More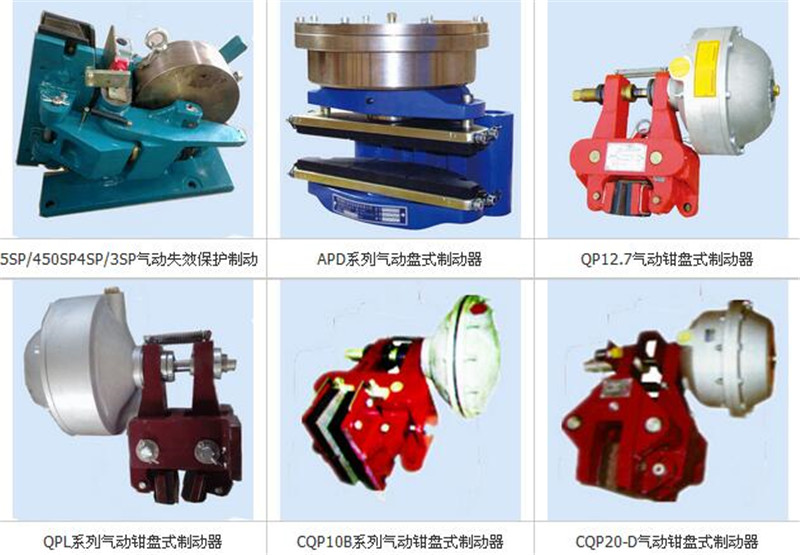
CQPL-12.71、 Working principleCQPL12.7 Pneumatic caliper Disc brake frame and cylinder are composed of two parts (see the structure diagram). When cylinder 1 is filled with pressure air, piston rod 5 quickly contracts into the cylinder under the action of air pressure. The left and right brake arms, under the action of return spring 4, drive the friction block 12 to quickly open (i.e. release the brake). When the cylinder stops supplying air and quickly deflates through the control valve, the piston rod 5 quickly extends under the internal spring of the cylinder, pushing the left and right brake arms to drive the friction block 12 to close (i.e., the holding brake).2、 Installation of brakesFirstly, check the brake surface of the brake disc and brake pad for oil sludge or other stains.2. Install the G3/8 "(cast iron rod cylinder) or 1/2" (cast aluminum cylinder) connector on the air inlet of cylinder 1, connect the air pipe with a hose, and the air source should be free of oil, water, and other impurities3. When installing, first introduce pressure air to retract the piston rod 5 into the cylinder. Then, install the friction block 12 in the direction perpendicular to the brake disc into the brake disc. Then, fix the base 9 horizontally on the rigid base so that its center is in line with the thickness center of the brake disc. The installation position dimensions are shown in the structural diagram3、 Modea) Adjust the air pressure value to a range of 5-7 bar.b) For normal work, the first step is to test the brake several times and check if there are any abnormalities in the brake.c) The retraction distance of the friction block can be adjusted by rotating the adjustment rod 6 to change the size of the working stroke. When rotating the adjustment rod, pressure air is first introduced to retract the piston rod, and then adjusted.4、 RepairWhen the friction plate is worn and the working stroke increases to 8mm, it is necessary to immediately adjust lever 6 to readjust the working stroke by about 4mm. Otherwise, the brake will fail. After adjustment, the nut 7 should be tightened. When the friction plate 12 is worn to about 6mm, the wear plate needs to be replaced. The replacement steps are as follows: www.hnbrakes.com1. Cylinder,2. Right brake arm3. Return spring5. Piston rod6. Adjusting the lever7. Nut8. Left brake arm9. Base10. Brake pads11. Spring steel wire12. Friction blockCQPL12.7 Structure Diagram of Air Caliper Disc Brake1. First, pull out the spring steel wire 11 on the brake block and remove the friction block 12.2. Place the new friction block in the U-shaped groove of the brake block, insert the spring steel wire, and then check whether the friction block is secure after installation.2、 Performance parametersparametermodelCustomized power NWorking stroke mmBacksetMmGalaxy effective radius of brake discMRated braking force distanceNmCQP12.7-ACQP12.7-Bsix hundredfour hundred4-51 0.2Brake disc radius 0.03Customized power × Having a radius6、 Shape and size parametersparametermodelABØ CØ Dcast ironcylinderaluminium alloycylindercast ironcylinderaluminium alloycylindercast ironcylinderaluminium alloycylindercast ironcylinderaluminium alloycylinderCQP12.7-Atwo hundred and ninety-fivethree hundredtwo hundred and twentytwo hundredØ186Ø190G3/8 "G1/2 "CQP12.7-Btwo hundred and seventy-fivetwo hundred and seventy-fivetwo hundredone hundred and seventy-fiveØ142Ø 144
time:2021-10-14
More
QP series pneumatic caliper disc brakeOverview: The QP (CQP) series pneumatic caliper disc brakes are mainly used for braking and deceleration of various mechanisms in lifting, transportation, metallurgy, mining, port, construction and other machinery.Usage conditions: Environmental temperature: -5 ℃ -40 ℃ Working pressure: 5-7bar for QP series; The CQP series is ≤ 7bar. Outdoor rain and snow erosion or corrosive gases and media should be corrosion-resistant products. The air source should not contain oil, water, or other impurities.Main features: The QP series features spring braking and pneumatic release; The CQP series is pneumatic braking with spring release. The overall structure is simple, small in size, and lightweight. Asbestos free brake pads, green and environmentally friendly. The installation of the brake pad adopts a spring clamp type, which is convenient and fast to replace. The brake pad is easy to adjust after being worn. Each disc diameter of the QP series brake can be adjusted for four levels of braking torque. All power sources do not need to be set separately and can be used in conjunction with existing air compression stations. Speed control valves are installed in the gas supply line, and the braking time can be adjusted steplessly.Note: 1. It can produce pneumatic caliper disc brakes with different disc thicknesses and installation sizes. 2. The specific model and structural dimensions reserve the right to change.product details For example: 1. Select QP12.7 type and A type air bags, with 6 springs and left air bag installation, and the order label is QP12.7-A-6 left;2. Select QPL12.7A and B type air bags with mechanical release display, and install the air bag on the right side. The order label is QPL12.7A-B-E1 on the right side.QP (CQP) 12.7 typeQP12.7 typemodelCustomized power (N) (eight springs)Galaxy effective radius of brake disc (m)Rated braking torque (Nm)Working gas capacity (cm3)Total gas capacity (cm3)Weight (kg)QP12.7-Asix thousand and four hundredBrake disc radius -0 03Rated power X Galaxy effective radiustwo hundred and seventy-threefive hundred and fifty-threetwenty-fourQP12.7-Bfour thousand and eight hundredone hundred and fortytwo hundred and ninety-threetwentyCQP12.7 typemodelCustomized power (N)Galaxy effective radius of brake disc (m)Rated braking torque (Nm)Working gas capacity (cm3)Total gas capacity (cm3)Weight (kg)CQP12.7-A1788X working air pressureBrake disc radius -0 03Rated power X Galaxy effective radiustwo hundred and seventy-threefive hundred and fifty-threetwenty-threeCQP12.7-B1055X working air pressureone hundred and fortytwo hundred and ninety-threenineteenQP12.7-C typeThe air bag is equipped with an automatic compensation mechanism, which eliminates the need for manual adjustment after the brake pad is worn, making it convenient and time saving.modelCustomized power (N) (eight springs)Galaxy effective radius of brake disc (m)Rated braking torque (Nm)Working gas capacity (cm3)Total gas capacity (cm3)Weight (kg)QP12.7-Csix thousand and four hundredBrake disc radius -0 03Rated power X Galaxy effective radiustwo hundred and seventy-threefive hundred and fifty-threetwenty-fiveQPL12.7A typeQPL12.7A typemodelCustomized power (N) (eight springs)Galaxy effective radius of brake disc (m)Rated braking torque (Nm)Working gas capacity (cm3)Total gas capacity (cm3)Weight (kg)QPL12.7A-Asix thousand and four hundredBrake disc radius -0.03Rated power X Galaxy effective radiustwo hundred and seventy-threefive hundred and fifty-threetwenty-fourQPL12.7A-Bfour thousand and eight hundredone hundred and fortytwo hundred and ninety-threetwentyCQPL12.7A typemodelCustomized power (N)Galaxy effective radius of brake disc (m)Rated braking torque (Nm)Working gas capacity (cm3)Total gas capacity (cm3)Weight (kg)CQPL12.7A-A1788X working air pressureBrake disc radius -0.03Rated power X Galaxy effective radiustwo hundred and seventy-threefive hundred and fifty-threetwenty-threeCQPL12.7A-B1055X working air pressureone hundred and fortytwo hundred and ninety-threenineteenQPL (CQPL) 12.7-B typeQPL12.7-B typemodelCustomized power (N) (eight springs)Galaxy effective radius of brake disc (m)Rated braking torque (Nm)Working gas capacity (cm3)Total gas capacity (cm3)Weight (kg)QPL12.7-Btwo thousand and one hundredBrake disc radius -0.03Rated power X Galaxy effective radiusone hundred and fortytwo hundred and ninety-threeelevenCQPL 12.7-B typemodelCustomized power (N)Galaxy effective radius of brake disc (m)Rated braking torque (Nm)Working gas capacity (cm3)Total gas capacity (cm3)Weight (kg)CQPL12.7-B416X working air pressureBrake disc radius -0.03Rated power X Galaxy effective radiusone hundred and fortytwo hundred and ninety-threetenQP (CQP) 30 (25.4) typeQP30 (25.4) typemodelECustomized power (N) (12 springs)Galaxy effective radius of brake disc (m)Rated braking torque (Nm)Working gas capacity (cm3)Total gas capacity (cm3)Weight (kg)QP30-Dthirtythirty-two thousand and eight hundredBrake disc radius -0. 065Rated power X Galaxy effective radiusone thousand and four hundredthree thousandseventyQP25.4-Dtwenty-five point fourCQP30 (25.4) typemodelECustomized power (N) (12 springs)Galaxy effective radius of brake disc (m)Rated braking torque (Nm)Working gas capacity (cm3)Total gas capacity (cm3)Weight (kg)CQP30-Dthirty6097X working air pressureBrake disc radius -0. 065Rated power X Galaxy effective radiusone thousand and four hundredthree thousandsixty-eightCQP25.4-Dtwenty-five point fourCQP20-D typeCQP20-D typemodelCustomized power (N)Galaxy effective radius of brake disc (m)Rated braking torque (Nm)Working gas capacity (cm3)Total gas capacity (cm3)Weight (kg)CQP20-D6097X working air pressureBrake disc radius -0. 065Rated power X Galaxy effective radiusone thousand and four hundredthree thousand
time:2021-10-14
More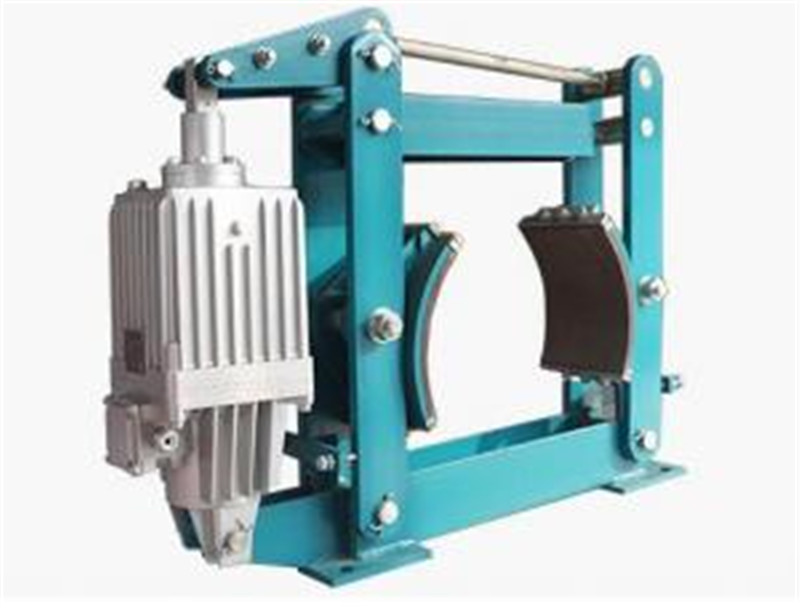
Transmission application of disc brake1. The transportation machinery industry. For example, feeder, conveyor, winch and crane all use disc brakes;2. The machinery industry. For example, electronic copying machines, printers and computers all use disc brakes;3. Machinery industry. For example, lathes and automatic CNC beds in the mechanical industry all use disc brakes.
time:2021-06-23
More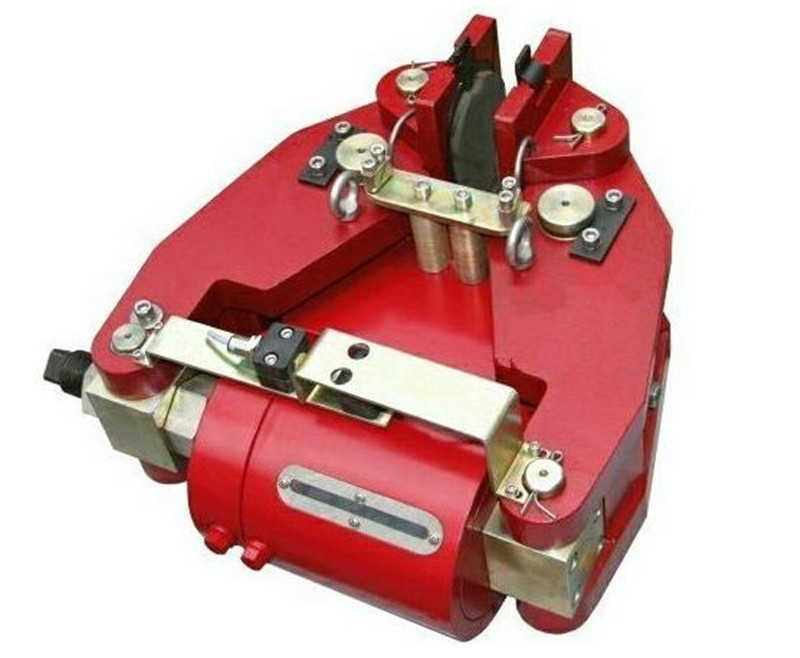
Precautions for use, maintenance, and upkeep of electric hydraulic thrusters1. The brake lining of the electric hydraulic thruster is a vulnerable component, and its usage limit should not be less than 0.8mm for the friction material part. Otherwise, the brake lining needs to be replaced.2. When cleaning the vehicle, never use cotton wool to clean the surface of the brake disc, to avoid polluting the brake lining and causing brake performance failure.3. The brake fluid of the electric hydraulic actuator in the reservoir should not be lower than the minimum limit. When adding brake fluid, attention should be paid to cleanliness, and dust and dirt should not be mixed into the reservoir to avoid blockage of the brake system and brake failure.4. Electric hydraulic thrusters should regularly replace vulnerable parts to prevent rubber parts from aging, usually within 1-2 years.5. During maintenance and upkeep of electric hydraulic thrusters, the tightening torque of fasteners should be checked at all times to prevent loosening.
time:2021-06-23
More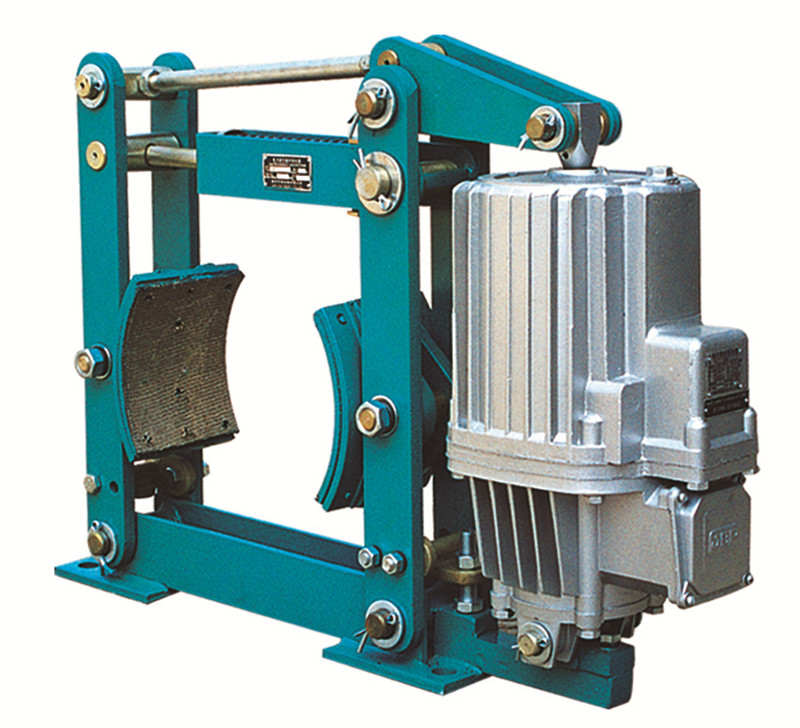
Use and Adjustment of Hydraulic Brakes1. Loosen the brake torque spring, manually lift the push rod triangle, adjust the upper adjustment screw to make the brake port gap 1.5 millimeters, and adjust the lower limit screw of the brake frame to evenly distribute the brake port gap on both sides; Adjust the torque spring to the required scale and tighten all locking nuts.When the brake pad wear meets the requirements, replace the brake pad and adjust according to the above steps; During the process of brake pad wear, due to brake pad wear, the brake triangle plate drops. When the accelerator rod drops close to the compensation mark, adjust the gap in a timely manner.
time:2021-06-23
More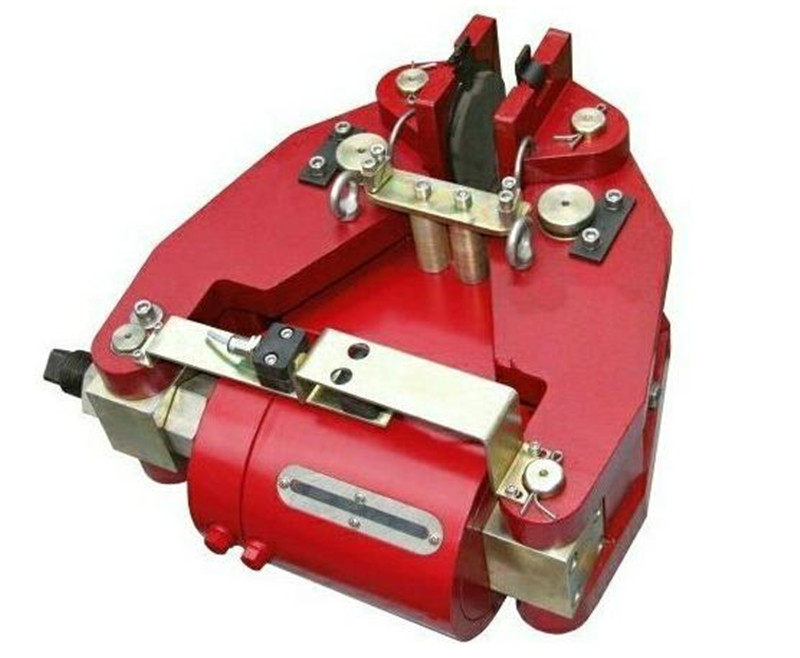
Precautions for the use of hydraulic brakes1. Lubricants are often added to electromagnetic brakes.2. Regularly check the length of the armature stroke. Because during the operation of the brake, the travel length of the armature will increase due to wear on the moving surface. When the length of the armature stroke cannot reach the normal value, it is necessary to adjust it to restore the minimum gap between the brake surface and the rotary table. If the stroke length of the armature increases above the normal value, it may greatly reduce the suction force.3. If a worn brake surface is replaced, the minimum gap between the brake surface and the rotary table should be adjusted from the beginning.4. Regularly check the tightening degree of the bolts, especially tighten the bolts of the electromagnet, the bolts of the electromagnet and the shell, the bolts of the magnetic yoke, the bolts of the electromagnet coil, and the wiring bolts.5. Regularly check the mechanical wear status of movable components and remove dust, burrs, and dirt from the surface of electromagnetic components.
time:2021-06-16
More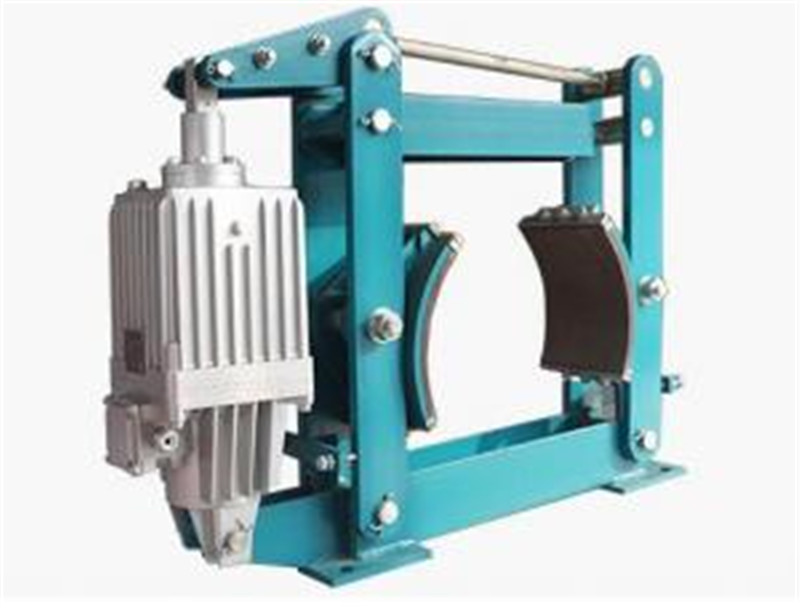
Talking about Brake Jitter of Disc BrakeBrake judder of disc brake is a typical brake system fault, which involves the generation and transmission of brake vibration and noise as well as the subjective feelings of passengers. Brake judder can accelerate the aging and fatigue damage of related components in the transmission path, affecting the driving comfort of the vehicle.The issue of brake jitter is generally caused by lower order disturbances in the braking system. Low frequency shaking is mainly caused by brake torque fluctuations, and the frequency of shaking is in some order relationship with the vehicle speed. The frequency is below 100 Hz, and most shaking occurs near the vehicle speed of 60 km/h.Brake judder can generally be divided into cold judder, hot judder, new car judder, wet judder (when there is water between the friction pairs), and rust judder according to the phenomenon. Cold shaking is mainly caused by irregular geometric dimensions of the brake disc or shaking of the friction plate, which affects the fluctuation of brake pressure and torque. Most cold shaking is a 1-5 order low-frequency vibration. Thermal jitter is caused by local thermal instability of the brake disc, resulting in thermal deformation. Thermal jitter generally occurs after multiple emergency brakes during high-speed driving, and the temperature of the brake disc rapidly increases. New car shaking is generally caused by uneven friction between the brake pads and brake discs during the new car's break-in period. Wet shaking is mainly caused by uneven braking pressure caused by water film between the brake disc and friction plate during rainy days, resulting in brake torque fluctuations. Rust shaking is caused by the Friction torque fluctuation between the friction plate and the brake disc after the brake disc is rusted. Generally, the shaking disappears after the rust is removed.
time:2021-06-16
More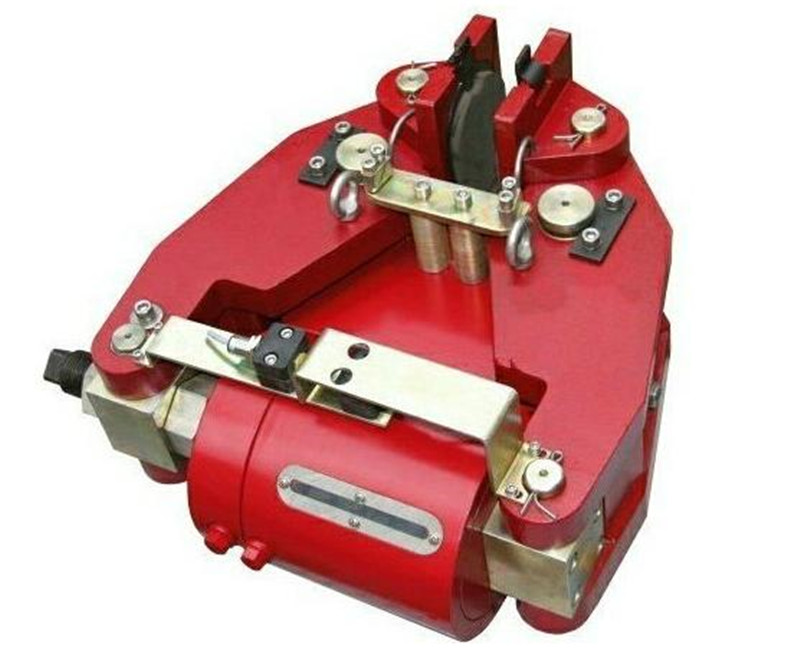
Selection of installation methods for electric hydraulic thrusters1. Vertical installation: The piston rod connecting block faces upwards;2. Horizontal installation and any position in the middle: the main parameter label faces upwards; All push rod connection blocks of thrusters can rotate.Regardless of the installation position, the piston rod cannot withstand any force to avoid affecting its effectiveness and lifespan.
time:2021-06-16
More